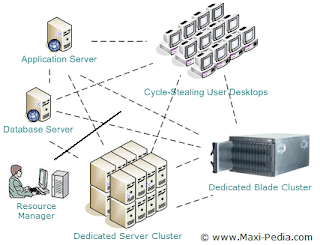
- Continuous informaiton flow
- Higher speed of communication
- Increased productivity through real time e.g tracking orders
- Cost reduction (less hardware needed)
- Universial access to software and important information
2. VoIP (Voice over Internet protocol) is a broadband phone service which travel over a high speed internet connection, rather than a regular phone line. The business benefits associated with VoIP include:
- Voice traffic can pass through existing Internet lines (ability to leverage an existing network to lower costs).
- Communication is free across the business network for many sites
3. A LAN or local area network is designed in order to connect a network of computers which are in close proximatey to one another e.g. Within an office, school or home.
A WAN or wide area network connects over a large geographical area e.g. A state or entire country.
Both technologies perform the same role by connecting a network of computers, however differ in respect to the geographical scope in which they cover.
4. RFID or Radio frequency identification, is a technology that uses a transceiver and a transponder (in the form of chips or tags) to identify an object, person or animal. Some examples of RFID technology include the RTA e-tag which remotely scans and charges each individual car tolls.
RFID can be used to help make a supply chain more effective by being attached to inventory in order to keep the tracking of stock as efficient as possible as it travels throught the supply chain. It can also help determine a more accurate and positive arrival time of stock - helping to improve punctuation of delivery.
5. Some advantages of deploying mobile technology include:
- Allows for real time data to be gained allowing for real time processing of the information thus a faster delievery.
- Higher accessability important business informaiton.
Some disadvantage of deploying mobile technology include:
- If not installed correctly may cause privacy issues
- Higher risk of hacking or viruses
Network coded wireless architecture